Search engine positioning is the practice of optimizing individual web pages so that they rank as high as possible in the search engines for particular keywords.
- Search Engine Positioning vs SEO
- Search Engine Positioning Strategies
- #1. Optimize for mobile search
- #2. Optimize for Voice Search
- #3. Optimize for ‘Rich Answers’
- #4. Address Searcher Intent
- #5. Write longer content
- #6. Write blog posts with high topical authority
- #7. Speed up your website
- #8. Reduce bounce rate
- #9. Improve your click-through-rate (CTR)
- #10. Improve ‘dwell time’
- #11. Make your page easy to scan
- #12. Target featured snippets
- #13. Use content mapping and interlinking
- #14. Keep your content up-to-date
- #15. Use your keywords strategically
- #16. Optimize your meta title and meta description
- #17. Use schema markup
- #18. Use a featured image
- #19. Link out to authority sites
- #20. Build high authority backlinks
- #21. Target long-tail keywords
- #22. Use LSI keywords
- #23. Turn your blog posts into YouTube videos
- #24. Use images in your blog posts
- #25. Use shorter URLs
- Conclusion
- More Articles About Ranking Factors

The reason search engine positioning is so important is that the click-through rate (CTR) from the search results falls away dramatically as you go down the SERPs.
You can see this in the following chart, measuring click-through rate against SERP position:
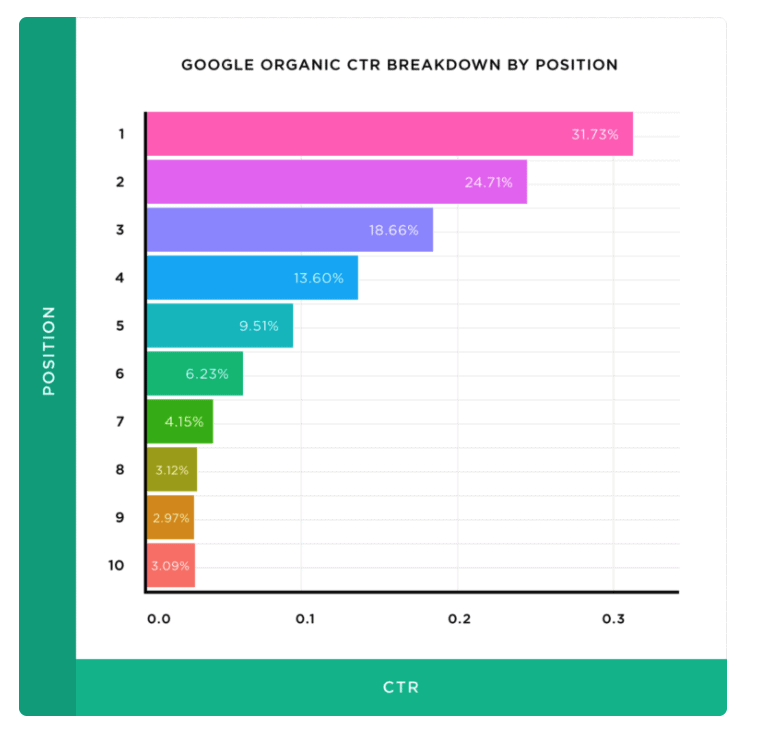
Image source: Backlinko
By the time you get half way down the page, your SERP snippet is getting less than 10% of the available clicks from Page #1 of the search results.
To put it another way: the lion’s share of the traffic on any search results page goes to the top three positions in the SERPs.
As we’ll see in this article, search engine positioning is about optimizing a range of On-Page SEO factors that can help your pages to rank higher in the search results.
In this blog post, you’ll discover 25 search engine positioning strategies, including how to:
- optimize for mobile search
- optimize for voice search
- prime your content for ‘rich answers’
- write content that has high topical authority
- speed up your website
- reduce bounce rate
- improve your click-through rate (CTR)
- increase ‘dwell time’
- make your pages easier to scan
and more!
But first of all, what’s the difference between SEO and search engine positioning?
Search Engine Positioning vs SEO
Search engine positioning is a specific skill within SEO.
SEO refers to everything you do to get your content on Page #1 of the search results, while search engine positioning refers to the techniques you use to get your pages as high as possible in the search results.
Think of it like this: if SEO is like building a piano, search engine positioning is like tuning the strings.
Search Engine Positioning Strategies
Here are 25 search positioning strategies that will help your pages to rank higher in the search results:
#1. Optimize for mobile search
Mobile search now accounts for 59% of organic search traffic:
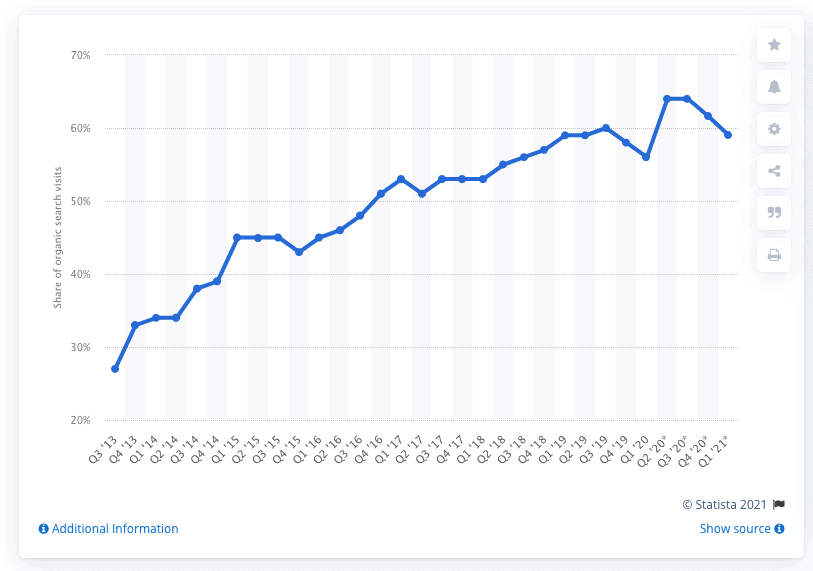
Image source: Statista
And that’s why optimizing for mobile is a key search engine positioning strategy.
Here are three key steps for optimizing for mobile:
Test your site using Google’s mobile-friendly tool
The first thing to do is check if your site is already mobile-friendly. Use Google’s Mobile Friendly Testing Tool.
If your page passes the test, you’ll see a green sign telling you that your page is mobile friendly:
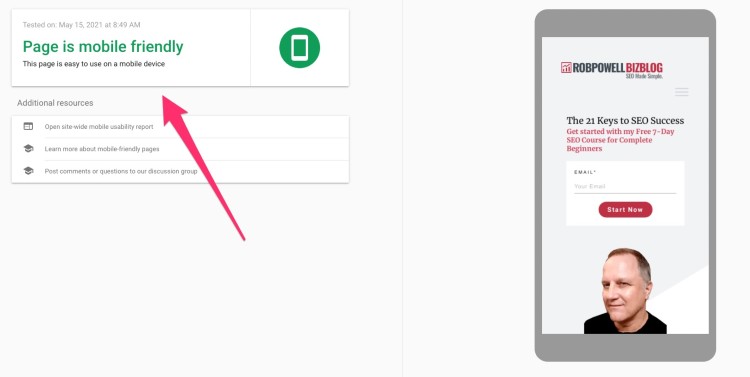
Use a mobile-friendly WordPress theme
A mobile-friendly theme is one which adapts responsively to different devices so that it always displays correctly on any device. Here are some of the most mobile-friendly WordPress themes:
Enable accelerated mobile pages (AMP)
Accelerated Mobile Pages or AMP is a mobile-friendly format created by Google in 2015 to ensure that content is served to mobile devices in the fastest and most responsive way.
To create AMP pages, just install the AMP for WordPress plugin.
#2. Optimize for Voice Search
The rapid uptake of voice-based digital assistants (like Alexa, Cortana, Siri, and Google Assistant) means that voice search is becoming a big part of organic search:
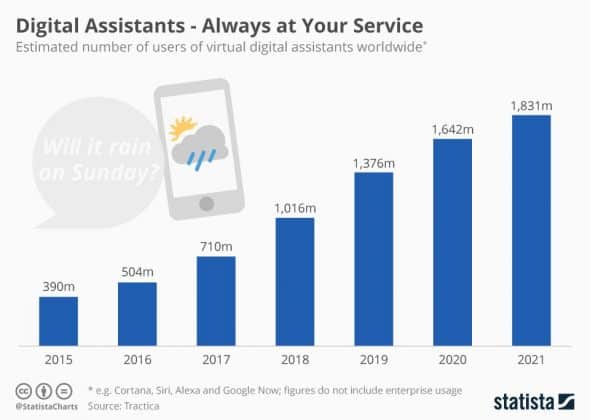
Source: Statista
In text search we all became adept at using very abbreviated search terms such as ‘best cms 2018’. But in voice search people are much more conversational: they’re more likely to say “what is the best content management system in 2018?”
Here are some of the ways you can optimize for voice search:
- Use more conversational phrases in your writing
- Include an FAQ page which algorithms can use to extract answers to common questions
- Use Structured Data Markup to give voice search devices quick clues as to what your content is about
- Use even longer tail keywords – voice search usually contains many more words than text search
For more tips on how to optimize for voice search read these two articles:
- Search Engine Land – ‘How to optimize for voice search’
- Neil Patel – ‘How to Optimize for Voice Search: 4 Simple SEO Strategies’
#3. Optimize for ‘Rich Answers’
Rich Answers are when Google gives you the answer to your search query directly in the search results – you don’t even need to click on the listing.
Let’s say you typed in: “what is pageless design”.
Google gives you an Answer Box (which is a type of Rich Answer):
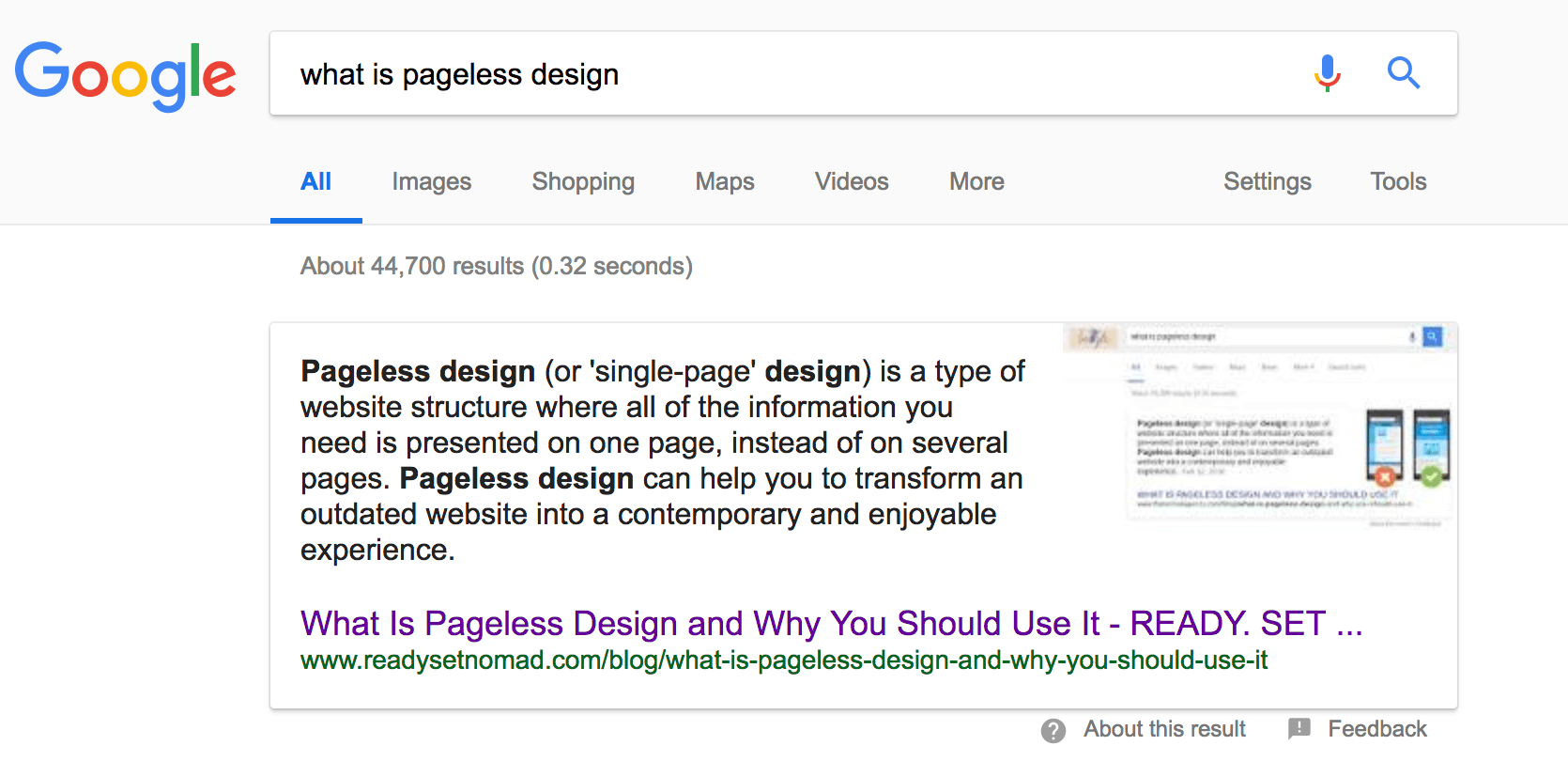
Optimizing for ‘Rich Answers’ is a search engine positioning strategy that not many bloggers are using, so do this and you’ll be ahead of the pack!
So how do you get your web pages to show up as Rich Answers in the search results?
Here are four key tips:
Use schema markup
This allows Google to easily extract relevant data from within your source code to be used in the Answer Box.
This is what a SERP snippet can look like when Schema Markup has been enabled:
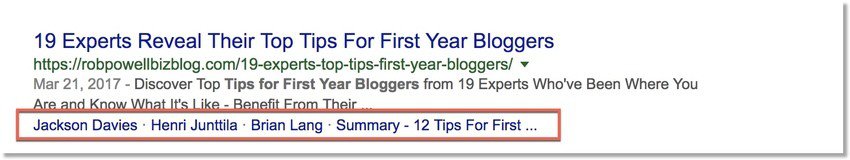
In the example above, Google has pulled out some of the experts I interviewed in the article and placed them in the SERP snippet. This helps my search result to stand out from the others.
Here’s another example:
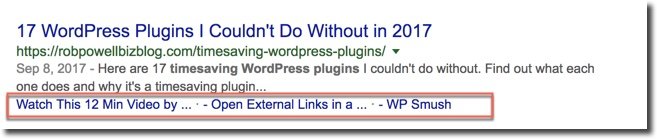
In this instance, Google has pulled two of the plugins I reviewed and placed them directly in the SERP snippet. Again, it makes my SERP snippet stand out and therefore it attracts more clicks.
Ask a question and then answer it
When you ask a question in your content, and then answer it, that primes the algorithm to create an Answer Box.
Create an FAQ page
It’s likely that Google looks for content for its Answer Boxes from within FAQ pages. So this is another way of increasing the chances of your content ending up in an Answer Box.
Turn your headline into a question
To get Google’s attention, turn your headline into a question that includes your keyword phrase, and then answer the question in the text beneath the headline
Here’s a way to find questions you might be able to answer: type a ‘seed phrase’ into Google using an asterisk as a ‘wildcard. In the example below I typed in ‘how do you * in wordpress’:
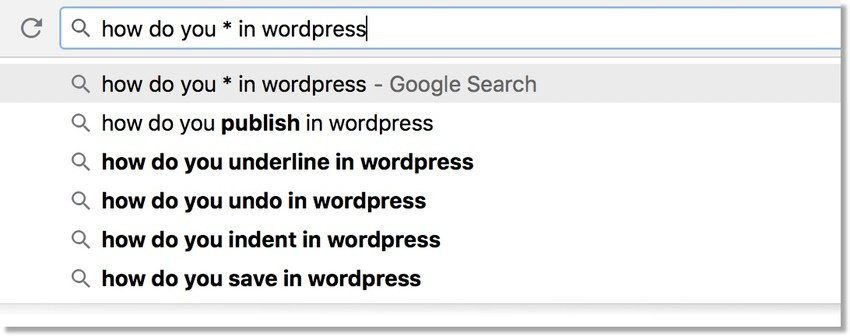
That gives you a list of popular queries about how to do things in WordPress.
To get even more ideas, click on one of them and then look at the ‘related searches’ below. These are often in the form of questions that searchers frequently ask:

#4. Address Searcher Intent
One of the keys to search engine positioning is understanding and addressing searcher intent:
Make sure your page answers the search query:
Searcher intent is HUGE.
My strategy is to go through a piece of content I want to rank as if I was a random site visitor. I determine which keyword they’ve (hopefully) used to navigate to my page, and then make sure that my page actually fulfills that search.
It involves high-level thinking. A page that discusses “how often should I change smoke detector batteries” shouldn’t just tell the reader how frequently they should change their batteries, but should also mention what kind of batteries are best to replace them with (lithium vs alkaline), how to replace the batteries, where to throw the old batteries away, etc.
Content that is well written and comprehensively fulfills searcher intent gives you a significant leg up over the competition.
Aaron Cote | Visual Glitch LLC
https://avisualglitch.com
Understand the searcher intent behind the keyword:
You need to understand the searcher intent behind keywords:
- check if the pages already ranking are informational or transactional.
- see if the metadata like URL, title tag, and meta description contain the target keywords.
- take note of what types of content are being featured within their articles.
- take note of the word counts of the top articles being featured for that keyword.
By doing this you are informing yourself about the benchmark for the type of content you need to produce in order to rank for the target keyword.
Then you can start to be creative and add new things you think will be valuable to the reader.
Phil Pearce | Analytics Director & Founder
https://measuremindsgroup.com
Make sure to answer the search query:
Before publication, I make sure I answer users’ queries in my post.
I discover these using a keyword research tool. You can use any tool for this, but I recommend Ahrefs.
When you do keyword research, click on the Question tab to discover questions about the topic.
If you want to rank on Google, using Google makes sense. Type in your keyword and find the People Also Ask section. Answer these in your post and in an FAQ section at the bottom of your article.
Make sure you let readers know in the intro, they’ll find the answers.
Publish longer-form content that gives users the answers to their queries. Shoot for 1500-2000 words or more of in-depth content. After publication, update your post with fresh content.
Use a SERPChecker to find out where your posts rank. Keep updating periodically until your posts rise to Page 1 in the rankings in the Top 3 spots.
End your post with a bio that shows your readers and Google that you are an expert on the topic in accordance with Google’s E-A-T criteria. These strategies boost your standings in the SERPs.
Janice Wald | Mostly Blogging
https://mostlyblogging.com
Is your page serving the user intent properly?
There are a lot of strategies to dominate on SERPs as Google is evolving day by day and working on the quality.
The most important strategy is to check at least the top 10 SERPs and analyze why they are ranking at the top. Check their internal links, outbound links, and most importantly the user intent.
Is your page is serving the user intent properly? While writing any blog you need to focus on the above-mentioned things.
Haris Tanveer | Team Lead Digital Marketer
https://www.cloudways.com/en/
Does your page give the searcher what they are looking for?
Never underestimate the power of quality content.
One aspect of quality content is that it’s based on actual search intent — meaning that when someone searches for your page’s focus keyword, they are getting the type of content they expect, based on their stage in the marketing funnel.
This all comes down to choosing the right keywords to focus on, based on what searchers intend to find with their query.
You can easily check this by googling your keyword and seeing whether product pages, informational pages, or comparison pages are the top results.
Once you have chosen a keyword that matches your page’s intent (the problem it solves for users), make sure to include that focus keyword in the title, URL, headings, and the first 150 words.
Doing this sends clear a clear message to google about your page, helping it to rank better.
Tanner Scott | Ranksey Digital Marketing
https://ranksey.com/
#5. Write longer content
Studies have shown that longer content ranks higher in the search results.
Brian Dean’s study of over 1 million search results shows a clear correlation between length of content and ranking. The average length of pages ranking in positions #1 to #3 in Google is 1900 to 2000 words.
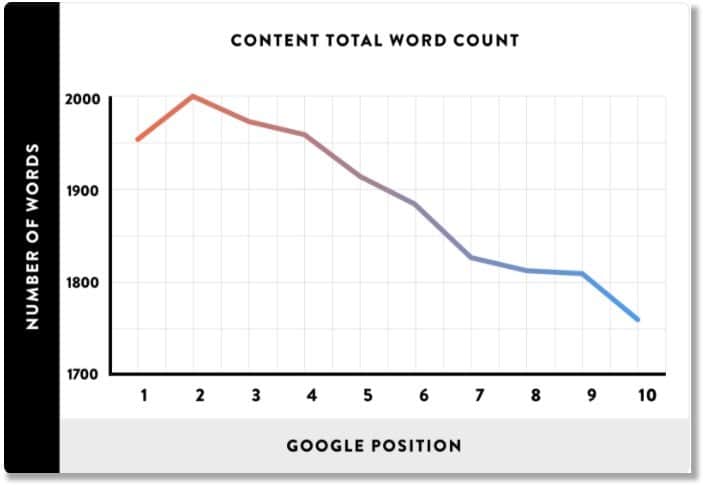
One of the reasons long form content ranks higher is simply that it takes longer to read. More time on page translates into higher rankings.
If you only implement one search engine positioning strategy from this article, make it this one! Aim for about 2000 words or more and you’ll be on the right side of the data.
#6. Write blog posts with high topical authority
As search engine algorithms get smarter, they’re able to measure how well a piece of content covers a particular topic. And that allows search engines to rank web pages on the basis of topical authority.
So, how do you increase topical authority?
- Be clear about the topics that make up your niche
- When you write on those topics, make sure you cover all the related sub-topics
- Create pillar pages, each one acting as a hub for a cluster of related blog posts
- Create internal links between posts or pages on your site that deal with related topics
- Include latent semantic indexing keywords in your blog posts
- Use the ‘Related searches’ feature in the Google results to find semantically related keywords
For more tips on how to increase topical authority, see my article How To Find Seed Keywords In Your Niche & Increase Topical Authority
Focus on topics first, then keywords:
One optimizing tactic that has proven to be successful is writing a post based on the topic alone, without targeting a keyword.
Then after a few months, look at your rankings and see for what terms the post ranks. You’ll sometimes see the article ranking in the 11-29 position range for a term, or a collection of similar terms, that have decent search volume.
Given that the article is ranking on the second or third SERPs, you have an opportunity to move it to the first SERP easily and quickly. If the term or collection of similar terms has high relevance to the article, you can then go in and optimize the article for them. This means updating the title tag and meta tag, but especially optimizing the on-page copy.
Get the new target term in the heading and sub-headings (making sure it sounds natural – don’t shoehorn it), and add it to the copy of the body.
Aim to add the new target term 3-4 times. When adding the new target term, don’t feel compelled to get it in the copy verbatim – you should use variations.
For example, if you decide to optimize an article about women’s shoes for the term “women’s business casual shoes summer,” you can use phrases like “these espadrilles make a classy and comfortable business casual shoe for women in the summer.”
Marcie Lord | Digital Dynamo LLC
https://digitaldynamollc.com/
#7. Speed up your website
Page speed is a ranking factor. Here are some tips for speeding up your website load time:
Check your site speed
The first thing to do is check your site speed.
Here are two of the best tools for checking your site speed:
If your page loads in 1.5 – 2 seconds, that’s considered a good site speed.
There are two main factors that affect the speed of your website:
- the way your
web host has configured their servers - the content you put on your web pages
You don’t have much control over the first item (except to change
But you can control the second item.
How to improve site speed
The main areas where you can speed up your website are:
- reduce image size
- use a content delivery network (CDN)
- reduce the number of HTTP requests
- reduce the number of plugins on your website
- minify CSS and Javascript
- enable HTTP/2
The best way to address these issues is to (1) use a speed optimization plugin such as WP Rocket, (2) use a content delivery network such as StackPath, and (3) use an image optimization plugin such as Short Pixel or Imagify.
#8. Reduce bounce rate
Google defines bounce rate as a single-page session on your site:
“In Analytics, a bounce is calculated specifically as a session that triggers only a single request to the Analytics server, such as when a user opens a single page on your site and then exits without triggering any other requests to the Analytics server during that session”.
To put another way, bounce rate is the percentage of visitors to a particular website who navigate away from the site after viewing only one page.
When a visitor bounces from your site, the content on your page was not what your visitor was looking for or expecting.
Since Google is in the business of matching search queries to search results, a high bounce rate sends a bad signal to Google. The algorithm will start moving you down the search results.
Brian Dean conducted a study of over one million search results and found that low bounce rates are strongly associated with higher Google rankings:
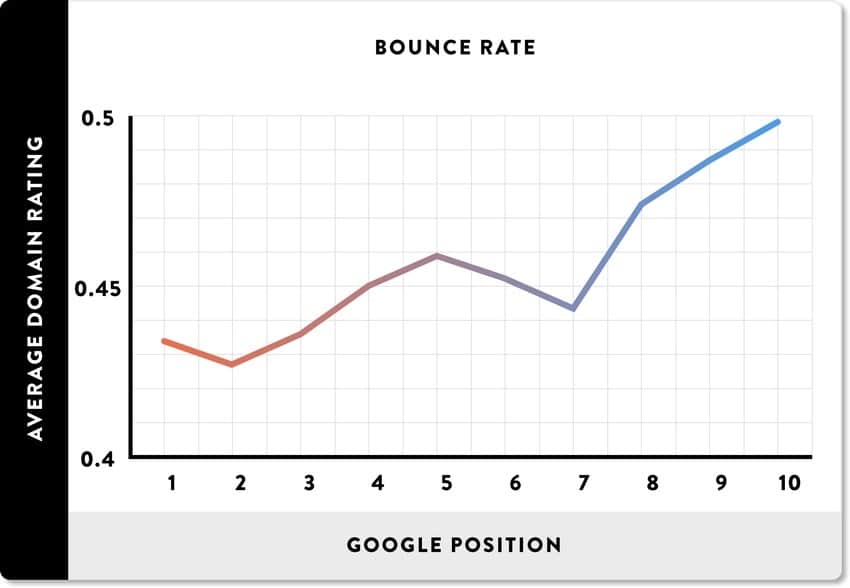
Find your bounce rate
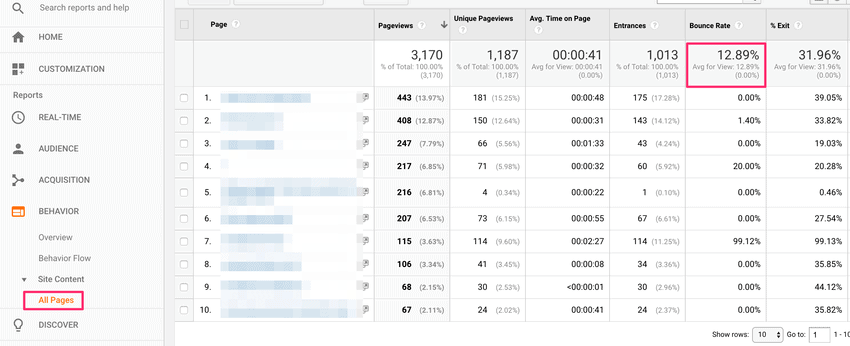
To find your bounce rate, log into Google Analytics and then go to Behaviour > Site Content > All Pages:
So what is an acceptable bounce rate?
It depends on what industry or niche you’re in. So it’s hard to come up with a single figure for everyone.
But here are some ‘ballpark’ figures for bounce rates provided by Go Rocket Fuel
- Bounce rate of 26 to 40 per cent is excellent
- 41 to 55 per cent is about average
- 56 to 70 per cent is higher than average, but still no cause for panic
- Bounce rate over 70 per cent is usually cause for alarm
How to Reduce Your Bounce Rate
Here are six ways to reduce your bounce rate:
- Make your content more readable by using shorter sentences, shorter paragraphs, plenty of headings, narrow column width, lots of white space, plenty of images, bullet points, and a large font.
- Speed up your web page loading time – according to Kissmetrics 47% of consumers expect a web page to load in 2 seconds or less.
- Make sure (a) you understand the searcher intent behind the keyword that you are targeting, and (b) that your page answers the question behind that keyword
- Have a clear message and a clear Call To Action – your reader needs to know immediately what your page is about and what you want them to do.
- Use transitional phrases in your writing to keep people moving down the page
- Use internal linking to take your visitor to other posts on related topics
#9. Improve your click-through-rate (CTR)
Click-through rate (CTR) is a key SEO factor in Google’s algorithm – the higher your CTR, the higher your page will rank in the search results.
This graphic from Neil Patel shows the relationship between CTR and Google Position:
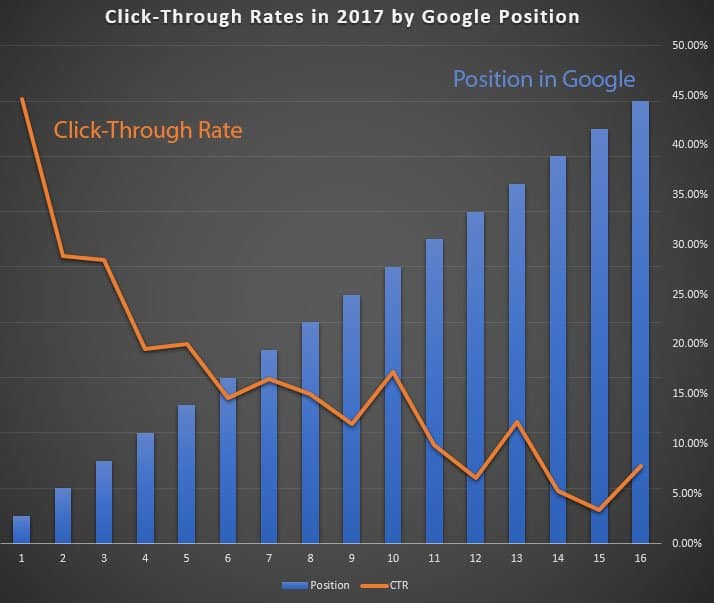
Improving your CTR from the SERPs is another vital search engine positioning strategy.
Google watches this metric closely and it directly affects your ranking in the search results!
Here are five tips for increasing your CTR:
1. Use this title tag formula
The wording of your SEO title or title tag plays a key role in whether or not people click on your web page. To get more clicks on your web page use this tried and tested formula for your meta title:
Number + [powerful adjective] + keyword
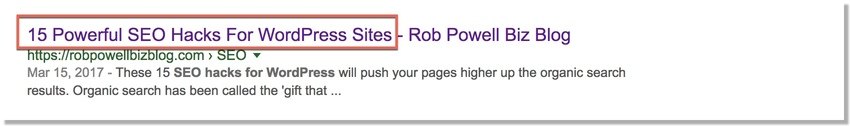
2. Use numbers and symbols
Use numbers and symbols in your meta title – they stand out in the SERPs:
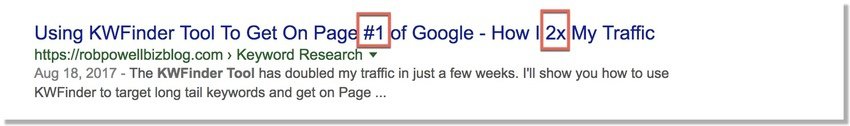
3. Place your keyword at the start
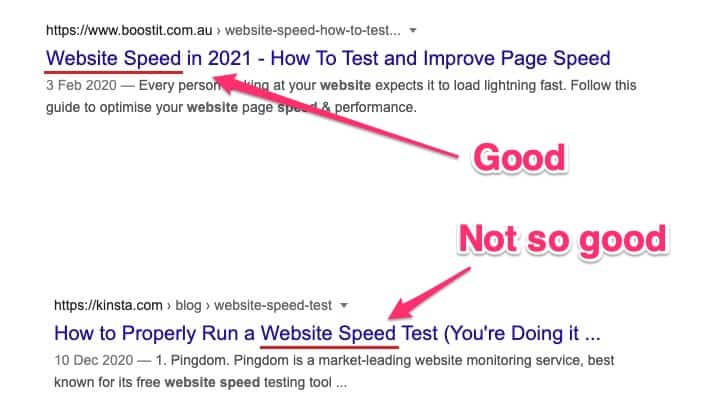
Use your keyword at the start of your SEO title (or meta title)
4. Include your keyword in the URL
Include your keyword(s) in the URL:
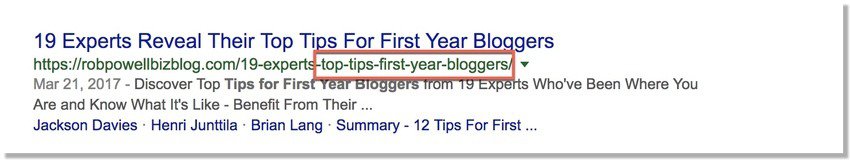
5. Use your keyword in the meta title and meta description
Use your keywords in the meta title and the meta description – Google will put them in bold:
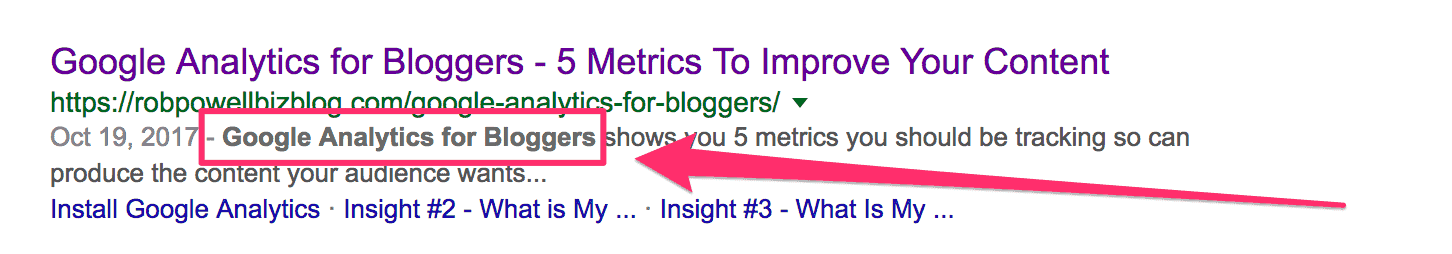
Use Calls To Action (CTA) in your title tags:
“One new strategy I am trying out is to optimize individual web pages is to provide call-to-actions in the title tag after the main keyword instead of a secondary keyword.
If the landing page has two main keywords (rare but sometimes happens) I would eschew this tactic in favor of having the two keywords in there.
Otherwise, if I can get more clicks that’s more traffic, more sales, and a bigger win for SEO. An ancillary benefit would be the more people that click, the more people visit and stick which also influences rankings.”
Joshua Mackens | Tutelary Marketing
#10. Improve ‘dwell time’
Dwell time, also called ‘time on page’, is one of the metrics that Google uses to rank pages.
The reason dwell time is important for search engines is that the more time a person spends on your page the more likely it is that your content answered their search query.
So the more time people spend on your page, the higher your page will rank in the search results.
For some great tips on how to increase time on page have a look at my article Seven Best Ways To Increase Time On Page & Get Higher Rankings.
#11. Make your page easy to scan
It’s hard to get the average visitor to go below the fold, as the following graphic shows:
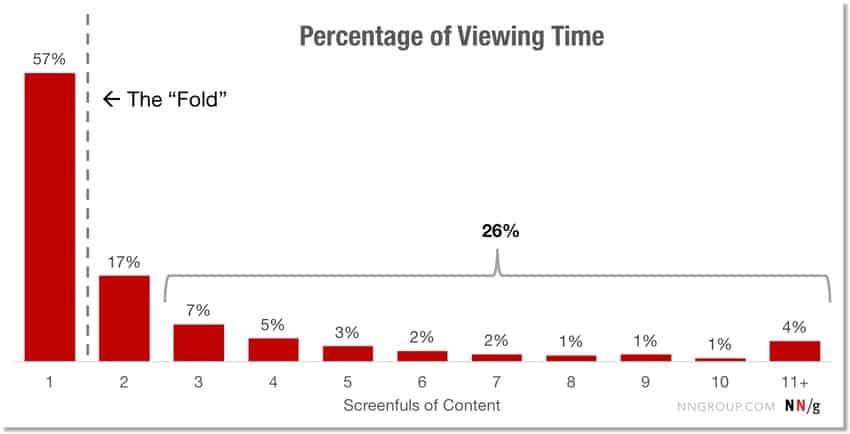
Dr. Jakob Nielson’s research shows that people spend a whopping 57% of their time above the “fold” (i.e. on the first screen of content).
How do you get visitors to keep scanning down your page?
Make your page easy to scan by breaking up walls of text using short paragraphs, headings and sub-headings, images, and large font size (16 px and over).
Here are some tips from Susan Greene on how to Make Your Web Content More Readable.
You can also make your pages much more scannable by using good visual hierarchy as UX Planet explains in the ‘Do’s and Don’ts of Web Design’.
People scan when they first arrive at a web page: they quickly want to see what the page has that’s relevant to them.
Here’s an example of how to draw in the visitor’s eye using visual hierarchy:
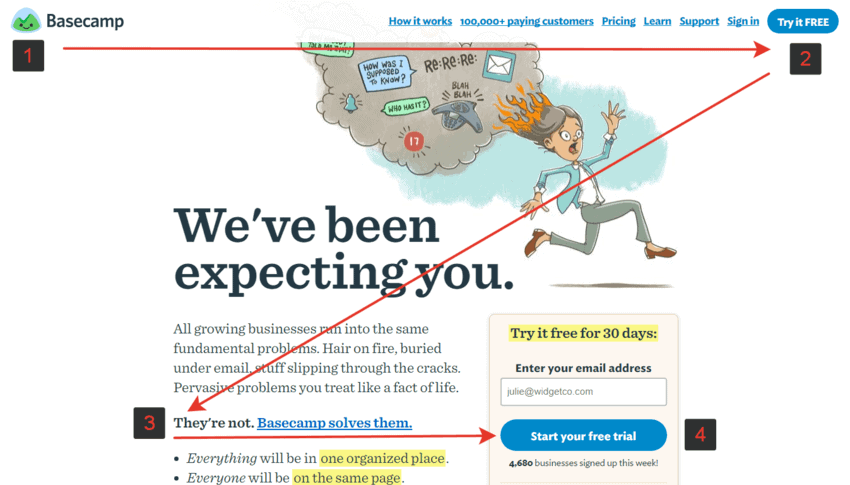
#12. Target featured snippets
Going after featured snippets is another powerful search engine positioning strategy. Prime your content with snippets of text that lend themselves to being used in a featured snippet:
Include feature-able snippets of text within your article:
Content writers and marketers should place more focus on landing content in the featured snippet (position 0).
Especially when competition for a keyword is high, constructing feature-able snippets within the body of an article can help push your material to the top even if you don’t have the backlinks to generally compete.
In other words, pick a long-tail keyword and give a clean 1-2 sentence response/summary of what the researcher is looking for.
As an example, in the work I do for an investment bank, we were able to get a featured snippet in position 0 for the keyword “saas retention rate benchmark” because a snippet of our content offered exactly that.
This article had 0 backlinks.
Jack Vawdrey | Content Marketing for Private Equity
Jackvawdrey.com
#13. Use content mapping and interlinking
Linking internally between different pages that share the same topic is another strategy that will help push your pages higher in the search results:
Keep your internal content structure well-maintained:
Content mapping and proper interlinking have proven successful in helping us rank our content higher.
Publishing SEO-optimized content is one thing, but regularly auditing, updating it, and keeping an eye on the interlinking is yet another. Every time you publish a new piece, it’s imperative that you update your existing, old content by linking out to your fresh blog post (if relevant).
A lot of content marketers tend to “publish and forget” or focus solely on off-site SEO (backlinks) when trying to get their new piece to rank higher in SERP.
Backlinks matter, but keeping your internal content structure well-maintained and properly interlinked is what can make a difference if you are competing for highly popular queries.
You can use tools like Surfer SEO or Screaming Frog to run internal audits and optimize your content and interlinking for better results.
Kas Szatylowicz | Content & SEO Manager
https://www.v7labs.com/
Use a ‘related articles’ box:
If I have an article at the bottom of page 1, one of the strategies that I use is internal linking.
I’ll add the link to the article in some additional blog posts as “related” or I’ll add it to the sidebar of my blogs as a “favorite article” so it gets some more juice. This strategy helps boost it up on the SERPs page.
Jessica Rhoades | Create IT Web Designs
https://createitwebdesigns.com
Use keywords in the anchor text of your internal links:
For on-page, we use the internal linking strategy to link our high authority pages to our low authority pages to give them an SEO boost. We just make sure that the links have keyword-rich anchor text.
Patrick Garde | ExaWeb Corporation
https://www.exaweb.com.ph
#14. Keep your content up-to-date
A huge percentage of online content hasn’t been updated for five years or more. So of if you regularly update your old blog posts (with new info, new images, new headings etc), you’ll be ahead of the pack:
Update your content and continuously improve it:
As always, quality is the greatest driver of SERP rankings.
We must remember though, that good quality content right now might not be so good in the future, most especially if the topic you’ve chosen is highly evolving.
That being said, one of the best strategies we’ve ever done is to update content and continuously improve them by adding current insights about the topics periodically.
This involves backtracking and retroactive tasks, but they’re definitely worth our while because they drastically improve quality – which is king when it comes to SERPs.
Ted Liu | Just SEO
https://www.justseo.co.nz/
#15. Use your keywords strategically
Make sure to place your keywords in these strategic locations:
To rank higher on search engines, you need to optimize the web page for specific keywords.
To create content that Google wants to rank, be sure to write clear, valuable, unique, and relevant content.
Remember keyword placement, which is called “technical optimization”. This way, you will let users and search engines know what your page is about.
Here’s what you should do:
1. Include Your Keyword in the Title
Try to be as brief and meaningful as possible. Avoid keyword stuffing by inserting the keyword several times in the title of your page.
2. Include Your Keyword in the URL
Try to create a short and descriptive URL for your content. Include your keyword and be concise.
3. Optimize Your Title Tag
The title of your page should look natural and bring value to your users. Give each page of your website a unique title. Include your keyword in it, possibly at the beginning.
4. Use Your Keyword In The First 100 Words
It may seem like an old technique, but it still works. Simply use your main keyword once in the first 100 words of your article.
5. Write an Optimized Meta Description
Use it to amplify the meaning of the title tag and search intent. Use an active voice, be brief and clear. Add your keyword in it without repeating it many times.
6. Use Your Keyword in Sub-Headings
Simply include the keyword in the H2, H3, H4 of your web page.
7. Optimize Your Images
Add your keywords in the file name and alternate text of the images on your web page.
8. Internal Linking
Thanks to this practice, you can help readers identify the content you care about the most. Plus, you help crawlers understand your website structure. Be sure to select the most important pages on your website and choose a relevant anchor text(with keywords in it) to interlink them.
Erik Emanuelli
https://erikemanuelli.com/
#16. Optimize your meta title and meta description
Your meta title and meta description are like little text ads for your web page. Optimize them so that Google can better understand what your page is about:
Help Google understand what your page is about:
Your page needs to be visible to Google’s ‘eyes’ so to speak. Use an accurate meta title and description incorporating important keywords so that the search engine can understand your web page. This refers to indexing. Help Google help you!
Eric Ang | One Search Pro
https://onesearchpro.my/
Optimize your meta tags for higher click-through rate (CTR):
One very important and overlooked strategy when it comes to page optimization is optimizing meta descriptions for click-through rate.
In Google Ads & PPC land CTR optimization is a key factor in driving ad performance. Weirdly, in the SEO world also nobody talks about click-through rates in relation to meta descriptions which is strange as it’s well known that a single word change in a Google Ad can easily 2x CTR.
If we apply the same principles to organic search, that means there’s an opportunity to 2x (or better) CTR from the organic SERP by writing CTR optimized meta descriptions.
Here are some simple techniques to boost CTR we use on our own sites and client sites::
– use capitals for the start of each word in your meta description, a Google Ads 101 technique almost never applied to SEO
– include power words and use ALL CAPS on them where appropriate, for example FREE, FAST, INSURED, GUARANTEED -> power words are fantastic for driving a point home AND in Google Ads, you can’t use them as they’re quite powerful but you’re free to use them in organic search
– if a phone call is a conversion for you include the phone number in both the title tag and meta description. On many devices that number will be a click to call number in the SERP and often you’ll get the call straight from the SERP
– don’t ask a question in the meta description! This is one of the most common mistakes we see: if someone has googled “best dog collars for golden retrievers” don’t waste half your meta description by starting it with “Are you looking for the best dog collar for your Golden Retriever?” as they’ve already told you this! Instead, if we optimize for CTR something like this would be more appropriate “In This Post We Review The 50 Most Popular Dog Collars For Golden Retrievers & Determine Which Is The BEST Based On Price, Quality & Features”
Brendan Tully | The Search Engine Shop
https://www.thesearchengineshop.com
#17. Use schema markup
Adding schema markup to your site helps Google add extra features to your SERP snippet. And that makes your snippet stand out from the rest:
Add schema markup to maximize impressions and clicks:
Creating a web page (ideally blog post or FAQ) with common questions in mind (around the topic or theme), then optimizing with schema markup can maximize impressions and clicks, especially if your post becomes the “best answer” in searches that generate rich snippets.
We used this strategy at Anvil with our blog and earned an average of 1 million impressions a month with just a few key posts.
Kent Lewis
Anvil | Measurable Marketing
www.anvilmedia.com
#18. Use a featured image
Google shows featured images in some SERP snippets in mobile search. This makes your page stand out from the others and can improve click-through rate (CTR).
Make sure your featured image contains the title of the your article in a legible font – this seems to improve SERP ranking. Google can read text embedded in images and so images containing your keyword could potentially improve your SEO.
For more on this topic, see this article: Did Google Just Read the Text on My Image and Can This Affect My Rankings?
#19. Link out to authority sites
Linking out to authority website will strengthen your search engine positioning.
Here are some of the reasons external linking is good for SEO:
- It makes your resource more valuable to your readers, and therefore more likely to be shared
- It provides an opportunity to build relationships with other bloggers
- It creates an incentive for other sites to link to you (reciprocity is a driving principle in human behaviour)
- According to Moz, linking to relevant authority websites is likely rewarded by the search engines in their algorithms.
#20. Build high authority backlinks
Backlinks are still one of the top three ranking factors. So link building is a vital search engine positioning strategy:
Getting backlinks from HARO (1):
The best practice is to focus on getting more authoritative backlinks.
HARO is one practical means to that. This allows me to get valuable media coverage from high-traffic websites that are great for branding.
Aside from being free, the audiences I get are organic. And organic audiences tend to become more loyal customers.
Marcus Clarke | Searchant.co
https://searchant.co/
Getting backlinks from HARO (2):
One effective tool we use to improve our SERP rankings is HARO (Help A Reporter Out).
You receive multiple emails a day with queries from hard-working journalists looking for experts in their field. This offers your company and its experts a chance to get backlinks through these articles when your quotes or tips are used.
We have found tremendous backlink success using this tool which in turn leads to higher SERP rankings.
Bryan Philips | Head of Marketing
https://inmotionmktg.com/
#21. Target long-tail keywords
This is the essence of search engine positioning!
The biggest mistake I see bloggers making is not doing keyword research before writing blog posts. And the second biggest mistake I see is when bloggers target head keywords instead of long tail keywords.
A head keyword is a keyword that contains only one or two words. An example would be ‘WordPress editor’.
Head keywords typically have a monthly search volume in the thousands. But they also have massive competition.
As a beginning blogger you simply have no chance of ranking on Page #1 of Google for a head keyword.
So what’s the solution?
Go for long tail keywords.
These are keywords that contain three or more words. They typically have a monthly search volume in the hundreds. Because their search volume is much lower, the competition to rank for these words is also much lower.
Here’s an example. Let’s say you’re writing an article about raising teenagers. Instead of targeting the keyword ‘raising teenagers’, go for the keyword ‘positive parenting strategies for the teenage years’.
But where do you find long tail keywords?
Here are my three favourite methods for finding long tail keywords:
Google Auto Suggest
You’ve probably noticed that when you type in a search query, Google gives you a handful of popular queries that other searchers have typed in:
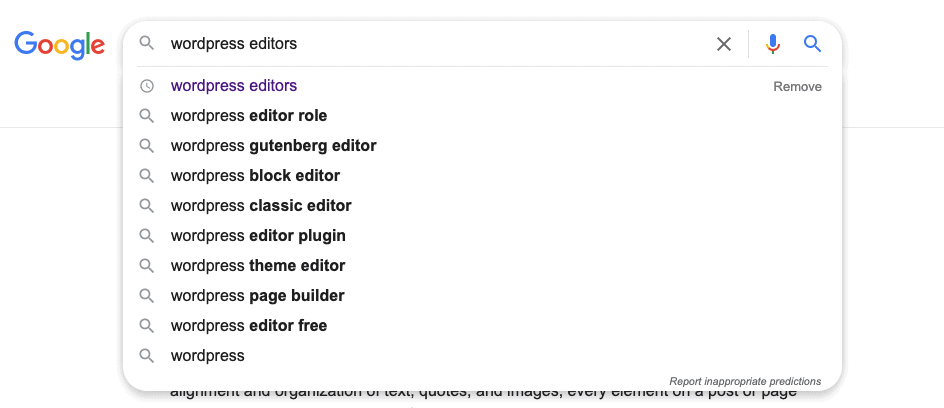
These are fantastic long tail keywords!
And you know people are searching on these terms because that’s where Google got them – from previous searches.
‘People Also Ask’ (PAA)
Scroll down the search results to the ‘People Also Ask’ section:
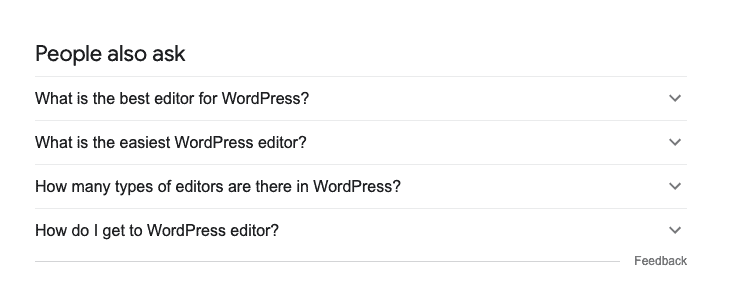
PAA is a great source for long-tail keywords.
You can take it a step further and click on one of the items in PAA. In this example, I clicked on the first item in the PAA box:
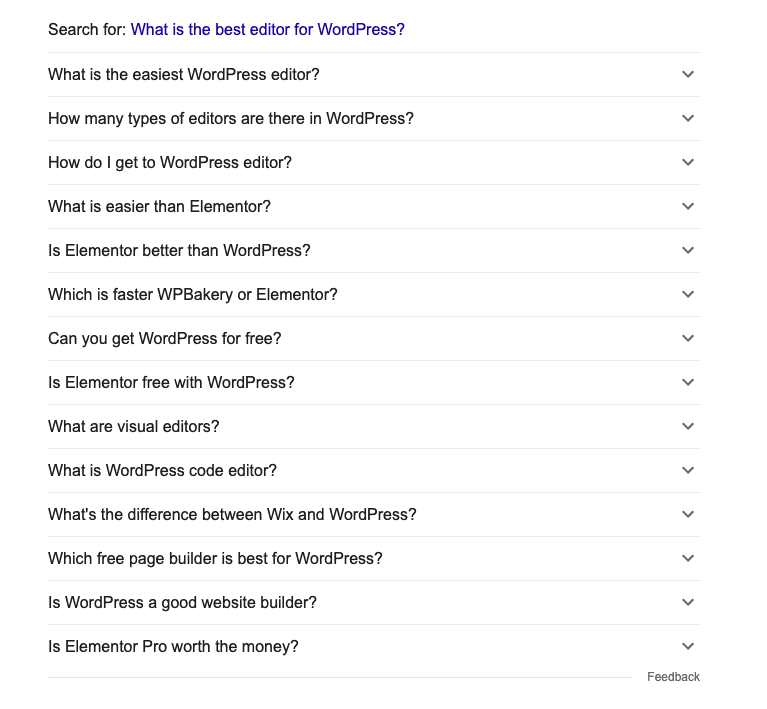
You’ll notice that every time you click on an item in PAA, Google adds more long-tail variations to the PAA box. This is an almost endless supply of long-tail keywords!
Google’s ‘Related Searches’
You may have noticed when you do a search that Google gives you a list of related keywords at the bottom of the page:
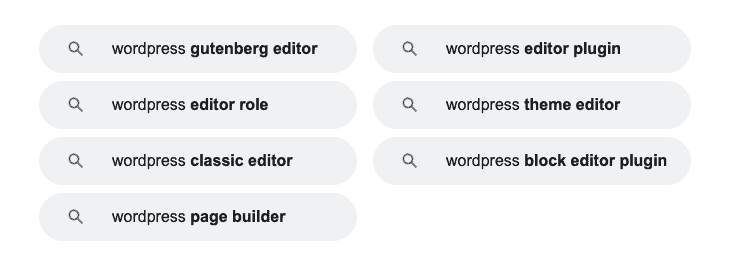
Google’s ‘related searches’ are a goldmine for long tail keywords!
#22. Use LSI keywords
Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) keywords are words that are semantically related to your main keyword.
LSI keywords are words that are often found in the same context as your main keyword, so they help search engines understand the context of your article.
Here are some LSI keywords for the keyword ‘coffee machine’:

With the Hummingbird algorithm (introduced in September of 2013) Google is no longer focusing on single keywords.
Instead, Google now understands context and patterns of words. It also understands the breadth and depth of the whole topic you’re writing about.
One of the factors that Google now uses to rank web pages is topical authority – how well you have covered the particular topic you are writing about.
And one of the techniques that search engines use to measure topical authority is latent semantic indexing. The algorithms know that certain words cluster together in predictable patterns, depending on what the topic is. And those word clusters are made up of latent semantic keywords.
So if you want your article to rank well in the search results, you need to use as many of the LSI keywords associated with your main keyword as you can.
The best way to find LSI keywords is Google itself. Start typing your keyword into the search bar and look at the long tail variations that come up in Google Auto Suggest. Those variations contain excellent LSI keywords.
You can also scroll down he search results till you see the ‘People Also Ask’ section – that’s another great source of LSI keywords.
And finally, have a look at the ‘Related Searches’ section at the foot of the search results page: those related searches also contain LSI keywords.
#23. Turn your blog posts into YouTube videos
Did you know that YouTube is a search engine?
In fact, it’s the second largest search engine on the web.
YouTube delivers massive amounts of free, targeted traffic to bloggers who are savvy enough to tap into this river of traffic.
And the best part?
Because relatively few people are making videos (compared with writing blog posts) the competition to get ranked on YouTube is far less than the competition to get on Page #1 of Google.
So all you need to do is invest in either Camtasia (for Windows) or Screenflow (for Mac) and turn your blog posts into YouTube videos.
#24. Use images in your blog posts
It’s been proven time and again that including images in your blog posts results in more shares.
In a study of over one million articles, BuzzSumo found that articles with an image once every 75-100 words got double the amount of shares of articles with fewer images:
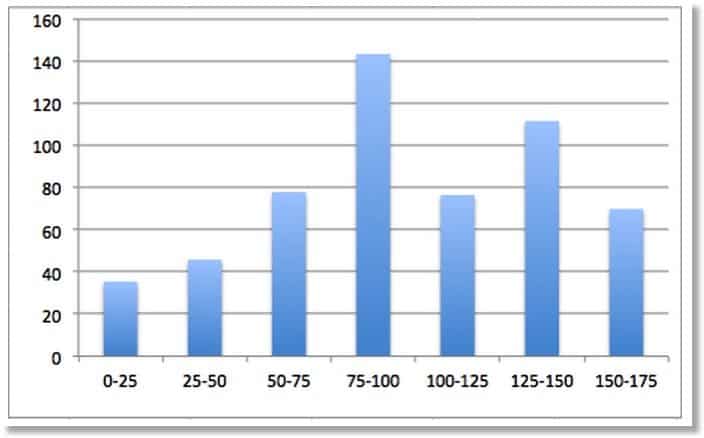
Here are three of the best sites for finding royalty-free images that you can use in your blog posts:
You can also make your own images using a graphic design platform like Canva. Creating your own images is far better for SEO and user experience than using stock images.
For more information on this topic, see this articleby Blue Compass: Are Stock Photos Bad for SEO?
#25. Use shorter URLs
SEO whizz Brian Dean analyzed over one million URLs and found overwhelming evidence that shorter URLs rank better on Google:
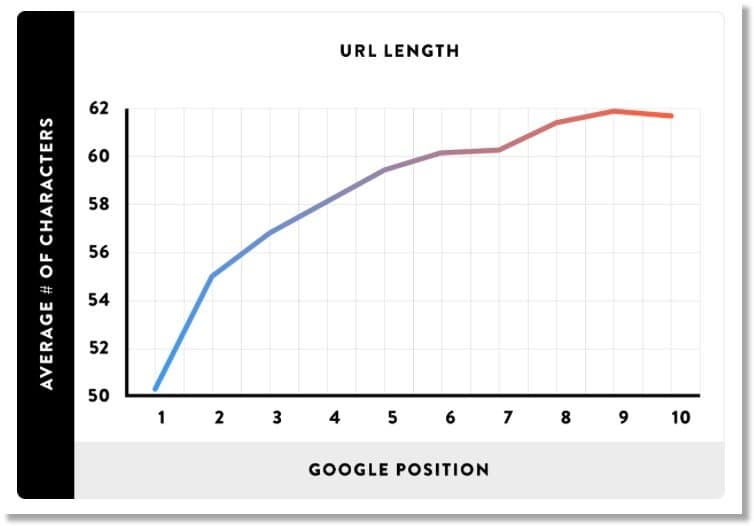
And here’s Google’s John Mueller himself making the same point:
…when we have two URLs that have the same content, and we try to pick one to show in the search results, we will pick the short one…It doesn’t mean it is a ranking factor, but it means if we have two URLs and one is really short and sweet and this other one has this long parameter attached to it and we know they show exactly the same content we will try to pick the shorter one.
George Mueller, Google
Conclusion
Search engine positioning is about making small adjustments that give you a slight edge over the other pages in the SERPs.
We’ve covered a lot of these techniques in this article – so many, it may seem overwhelming. But don’t be put off – even if you only implement 2 or 3 of these strategies, you’ll soon see results as your pages start climbing up the SERPs.
I’m always looking forward to your latest post. BTW, I’m following you on Twitter. Couldn’t find your opt-in form to subscribe.
Anyway thanks for another great post Rob!
Hey Victor, thanks so much – glad you found it useful! I’ve just added an opt-in form at the foot of the blog post 🙂 All the best, Rob.
Great Post. Thanks for providing such a nice information
Thanks Kavita, you’re most welcome, glad it was useful, Rob.
Another great tips Rob. I’m trying to implement some of the strategies that you have shared above. I will be back for more tips and tricks from you.
Thanks, Samm. Glad it was useful, Rob.
Hello,Rob Powell,
may i ask a question again.
with “4. Write Longer Content”,
i know long page with content are good for seo,
but is it also fine for product pages ?
thanks
Hi Su,
Thanks for your question.
Yes, even with product pages, it’s best to go for longer content. That can be difficult for a product page, especially if it only takes a few hundred words to describe the product. What you can do is describe the product and then have a series of headings underneath the product description where you talk about related issues, e.g.: ‘How to Use the Product’, ‘Product Care and Maintenance’, ‘Related Products’ etc.
The principle behind writing longer content is not simply that your page has more words than any other page in the search results: the real point is that by writing more words, you are covering more sub-topics and so you are increasing the topical authority of your page. It’s the topical authority, not simply the number of words, that the Google algorithm is taking notice of.
Hope this helps,
Rob.
WOW! Thorough-concise and full of great information-fantastic article! Thanks for the share and for taking the time. This information will be extremely to me in my own copywriting business-lots of amazing nuggets here!
Hi Sarah, thanks for your feedback! I’m glad it was useful – Rob.