The SEO acronym stands for Search Engine Optimization and it refers to everything you do to make the content on your website more visible in organic search.
SEO covers 5 main activities:
- Making your website architecture SEO-friendly
- Doing keyword research
- Creating SEO-friendly content
- Optimizing your content
- Building backlinks to your content
What Exactly is SEO?
So what exactly is search engine optimization?
Put simply SEO is anything you do to help your pages rank higher in the search results. And one of the ways to do that is to help the search engines understand what your content is about.
But there are many other aspects to optimizing a site for search engines.
For example, a big factor in optimization is user experience. If your page takes too long to load or people find your content difficult to read, your visitors won’t stay on your page for long. And the search engines will notice that and rank your page lower in the search results.
The Goal of SEO
Businesses spend vast amounts of time and money on search engine optimization (SEO).
And the purpose of all that SEO is simply to rank higher in the search results. Because higher ranking means more visitors and more visitors means more customers.
And that brings me to another SEO acronym: SERP, which is short for Search Engine Results Page.
Here’s a breakdown of the clicks you get from the SERPs, based on where your page ranks in the results:
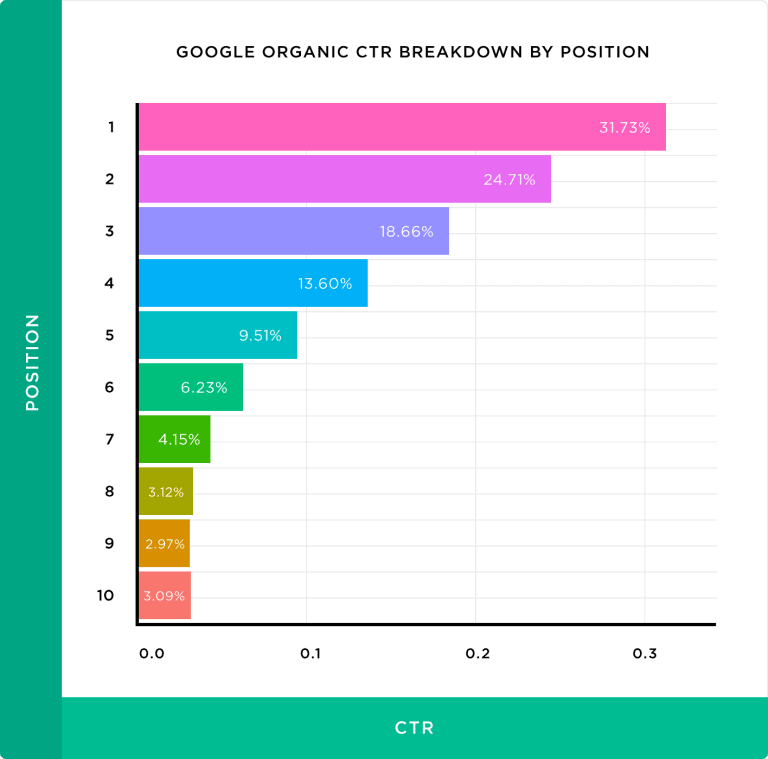
Backlinko reports that on average, Position #1 in the search results gets 31% of all the clicks on Page 1 of the search results. Position #2 gets nearly 24% and Position #3 gets 18%.
So, on average, the top three positions in the search results get a massive 73% of all the clicks!
There are usually 10 search results on each page and in this graphic you can see that the top 10 results get the lion’s share of the clicks. In fact, by the time you reach Page #2 (Position #11 to 20) the percentage of clicks has fallen away dramatically:
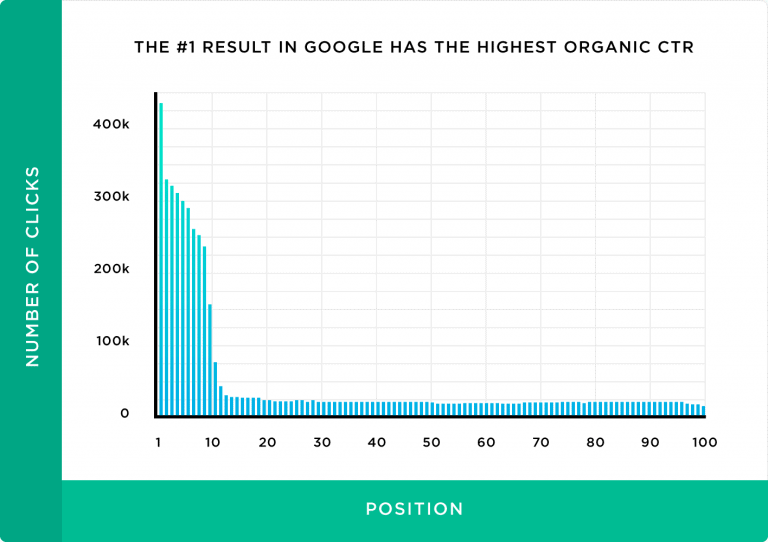
In a nutshell, the goal of SEO is to get into the top 10 positions and preferably the top three positions in the search results.
How Do Search Engines Work?
Search engines are like vast libraries. But instead of having to browse through hundreds of bookshelves, you just type a search query into a box.
Crawling the Internet
Search engines are constantly crawling the Internet, following the links within websites and between websites. As these robots (or ‘bots’) crawl the Internet, they ‘index’ each page that they find.
Going back to the library analogy, for each page that they find, the bots create an index card, like the ones you used to search through in a library catalog (back in the 1980s).
Indexing web pages
And when you do a search in Google or Bing or Yahoo Search, the search engine presents you with a summary of that index card. That summary is called a SERP snippet.
Of course, for every search query a person types in there will be thousands, hundreds of thousands, or even millions of matching pages.
How do the search engines decide which pages to show that at the top of the results?
They use ranking factors. Most of those ranking factors are a closely guarded secret. It’s not even known exactly how many there are. But most experts believe there are over 200 Google ranking factors.
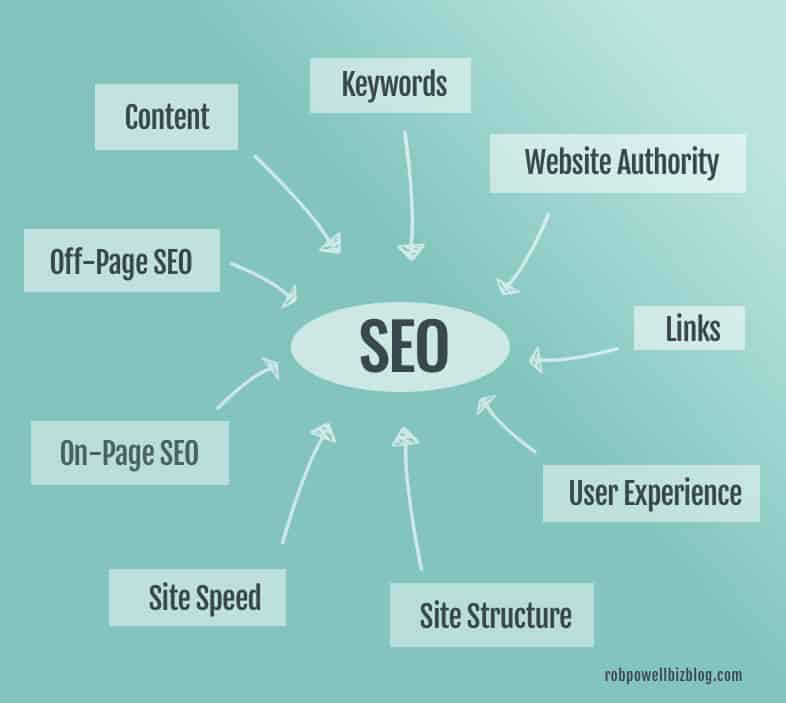
What Can You Optimize in SEO?
There are hundreds of things you can optimize on a website for better SEO results, but in this section, I’m going to focus on seven key areas that you can optimize for SEO.
1. Keywords
It’s useful to think of search engines as bringing together two kinds of people: people who are looking for information and people who have that information.
The mechanism that brings those two kinds of people together is keywords or keyword phrases.
And that’s why optimization begins with keyword research.
To rank your content in Google, you have to know what keywords your target audience are typing into Google.
And you can find those keywords by using a keyword research tool.
In the early days of search engines, it was all about keyword density.
But the algorithms are more sophisticated now, and they look for semantically related keywords: words that are related to your main keyword. When your content has plenty of related keywords, it shows the search engines that you have covered the topic well.
2. Page content
Optimizing content for SEO is about creating content that covers a topic well.
The number of words in a piece of content is not itself a ranking factor but top-ranking pages tend to have more words than lower-ranking pages simply because they cover the topic in greater depth.
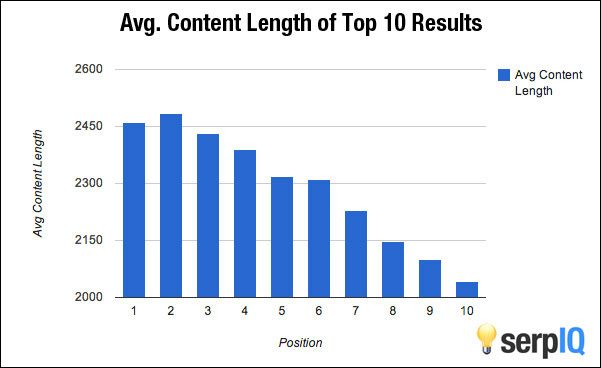
A study by SERP IQ found that the average number of words for content in the first place of Google was 2,416 words, while articles ranking in tenth place were on average only 2,032 words long.
Optimizing your content also means writing in an easy-to-understand style, using fonts and font-size that are easy to read, making sure your content has plenty of ‘white space’, breaking up your text with images, and so on.
3. Website authority
The authority of your web page refers to the trustworthiness of the content on your page. Is the information accurate? Are the opinions expressed reliable?
The main method search engines use to gauge the authority of a web page (and a website) is the number and quality of the links pointing to that page from other websites.
Each link is regarded as a vote of confidence. And if the websites linking to your content themselves have high authority, those links count for even more.
One commonly used metric for measuring website authority is ‘domain authority’ (DA). If a website with DA of 91 links to your website, that counts for much more than a link from a website with DA of 21.

4. User experience
Search engines carefully monitor the behavior of your visitors when they land on your page from the search results. This is called user experience, or UX (to use another SEO acronym).
To put it simply, the longer your visitors spend on your web page and the more they interact with your content (clicking on a table of contents, submitting an opt-in form, clicking on an internal link), the higher your UX and the better your page will rank
5. Site structure/architecture
Site architecture refers to the structure of your website and the hierarchy of your pages.
A good site structure, and one used by many websites, is a three-tier structure where tier one is the home page, tier two comprises the category pages and tier three consists of the individual topic or product pages:
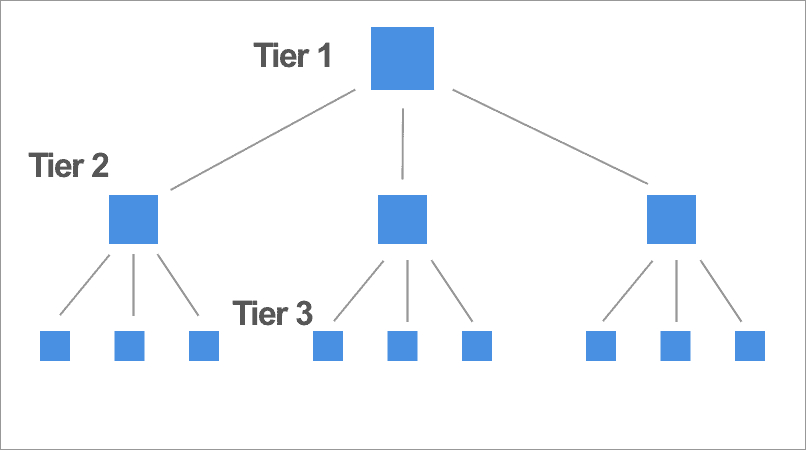
Site architecture is important for SEO because search engine crawlers can only find pages that are linked to from another page. So every page you create must be part of an interlinked structure.
Also, your site structure helps the search engines understand what your website is about.
6. Site speed
With more than 50% of all searches now being performed on mobile devices, speed is becoming a big factor for search engines.
When people use mobile devices they tend to be ‘on the go’ and not connected with home broadband. They’re often using slower Internet connections than they normally would.
And that’s why Google, for example, has announced that page speed is a ranking factor. It’s why Google introduced the Page Speed Insights index.
So making your website load faster is another key area of search engine optimization.
7. On-Page vs Off-Page
This last category is not an optimization factor in itself: rather, it’s a way of thinking about search engine optimization.
People often divide search engine optimization into On-Page and Off-Page optimization, and it’s a useful distinction.
On-Page optimization refers to everything that happens on the page itself: the content of that page, the keyword research for that page, the meta tags for that page, the load time for that page, etc.
Off-Page SEO refers to everything that happens off the page and it often means things that happen off-site as well. One of the biggest Off-Page optimization factors is backlinks: links coming to your page from other websites.
The Evolution of SEO
SEO is constantly changing. The search engines continually create algorithms that are better and better at understanding online content as well as search queries.
Core updates
‘Core updates’ are broad algorithm changes that affect websites across the board. Examples are:
- July 2021 Core Update — July 1, 2021
- Page Experience Update — June 25, 2021
- June 2021 Core Update — June 2, 2021
Specific algorithm updates
There are also specific algorithm updates like Penguin, Panda, or the Medic update that target specific issues.
SEO Is never static
All this means that SEO is never static.
While you don’t need to obsess about every new development in search engine technology, it’s good to be aware of the main directions and trends in how search engines are developing.
The most important thing, however, is to keep your users in mind: understand the searcher intent behind the keywords that you target and focus on delivering the best possible answers to those search queries.
Conclusion
This article has explained not only the meaning of the SEO acronym but also what SEO involvves.
Search Engine Optimization, often abbreviated to the acronym SEO, is the process of improving your content in the following areas so that it ranks better:
- Keywords – doing keyword research to discover what search terms people use when looking for the content you publish
- Content – creating content that answers the search query better than other pages that rank for the same search terms
- Authority – getting links and other off-site signals that tell the search engines that the information on your website or page is reliable and valuable
- User experience – encouraging people to stay on your page longer by making your content more useful and easier to read
- Site structure – using an SEO-friendly site architecture so that search engines can discover your content and understand how it is organized
- Speed – improving the speed of your website, so that your pages load quickly.
In summary, the SEO acronym refers to search engine optimization: it covers everything you do on your website and off your website to increase your search engine visibility.
More Articles About SEO
- Search Engine Visibility – 23 Valuable Tips For More Traffic
- Stuck on Page #2 of Google – How To Get Out in 7 Easy Steps
- 13 Types of SEO You Need To Know About in 2022
- SEO Recipe For Success – The 7 Key Ingredients For Ranking Well
- What Is SEO? An Introduction to Search Engine Optimization
- Seven Google SEO Trends To Watch For In 2022
- How To Write SEO Friendly Blog Posts – 17 Important Tips
- SEO Off-Page Techniques: 7 Important Facts You Need To Know
- The Advantages of SEO – 13 Important Facts You Need To Know
- SEO for Blog Posts – 15 Factors To Help You Rank Higher
- 19 SEO Mistakes You Should Avoid At All Costs
- Bing Search Engine Stats – Some Interesting Facts & Figures
- Benefits of SEO for Bloggers – 10 Reasons You Need To Be On Page #1