A content management system (CMS) is a piece of software that allows you to create, edit, and publish digital content to a website.
Put simply, a CMS allows you to build out a website without having to do any coding. It has built-in functions that allow you to add, edit, update, and remove content, such as blog posts and web pages.
Here’s a comparison that will help you understand what a CMS does.
Without a content management system, every time you create a new web page or a new blog post, you would have to write the page and its content in HTML code. That’s a lot of work. And it’s the reason websites used to be static.
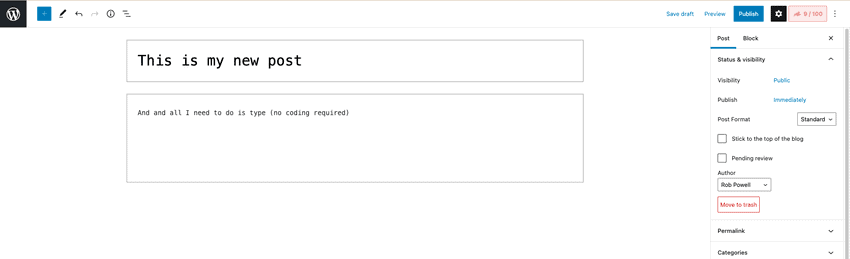
But with a CMS, you simply type away into a graphic user interface (GUI), such as this one in WordPress:
The CMS then publishes your content to a web page:

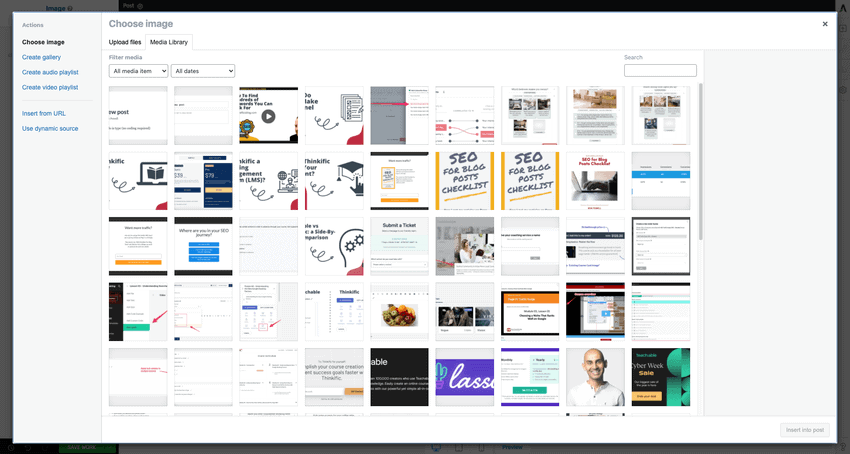
A CMS also contains a media management system that allows you to upload media such as images, audio files, and PDFs. You can then insert these media into your web pages or blog posts.
How Does a Content Management System Work?
So how does a CMS work? A content management system consists of two parts:
- a Content Management Application (CMA)
- a Content Delivery Application (CDA)
The content management application is the part that allows you to add and remove content from your website. It’s a user interface (GUI) that allows you to create and modify website content without using HTML or any other coding.
The content delivery application delivers the content produced in the CMA and renders it on a screen as a published web page or blog post.
What Are The Core Functions of a CMS?
The core functions of a good CMS are:
- Content creation – allows the user to create content in various formats
- Content storage – allows the user to store content on a website
- Media management – allows the user to add media such as photos, video, and audio files directly into the content
- Collaboration – uses a system of permissions that allows people to work together in different roles (e.g. authors, editors, admins)
- Publishing – converts the content into a published format, such as a blog post or a web page.
- Extensibility – the core functions of the CMS can be extended through the use of plugins, add-ons, and extensions.
With a CMS you can customize a website so that it looks exactly how you want it to look, without having to understand or execute a single line of code.
Why Use a CMS?
The alternative to a CMS would be an HTML website, built for you by a web developer.
Here are some of the benefits of a content management system compared with a static website that has been built from scratch using HTML:
No coding required
With a CMS, people who have no coding experience or knowledge can easily add, remove, and edit the content on a website. The graphical user interface (GUI) in a CMS allows you to manage your website without the help of a developer.
Easy to update
Updating content in real-time is easy with a CMS: you don’t have to wait around for a web developer to do it for you. Before the introduction of content management systems, websites were essentially static. With a CMS, your website is dynamic: you can add, remove, and modify your content with a few clicks.
Easy collaboration
With a CMS, you can assign roles to different people, such as ‘author’, ‘editor’, ‘admin’, and so on. This makes for easy collaboration within a team. Through a system of user permissions, a CMS allows you to give access to different functions to different people.
Extensibility
Most content management systems have modules or plugins that extend the core functionality of the CMS. This makes a CMS a powerful platform for your website.
Security
Websites are constantly at risk from cyberattacks. A custom website that has been built from scratch is more vulnerable to cyberattack than a website that uses a CMS. This is because CMS developers have teams of developers testing their platforms against all kinds of cyber threats.
Cost-effective and affordable
A CMS is designed to allow the user to customize a website, create and edit online content without using a developer. This means that running a website on a CMS is much cheaper than relying on a web developer every time you want to change something on your website.
Accessibility
A CMS can be accessed through a web browser. This means that a CMS-based website can be managed from anywhere in the world.
7 Key Features To Look For In a CMS
The content management system you choose will depend on what you want to do with your website. But regardless of that, here are seven features you should look for when choosing a CMS:
#1 – Intuitive Dashboard
Your CMS should have an intuitive and easy-to-use dashboard. This is where you create content, upload media files, assign roles to different users, install plugins, and so on.
Ideally, you want a single menu from which you can access all these different functionalities with one or two clicks.
#2 – Responsive Themes
You need a CMS that offers website themes that are responsive across all devices (desktop, smartphone, tablet).
This is important from an SEO point of view, given Google’s move to mobile-first indexing.
#3 – Version Control and Backups
When creating blog posts or web pages, you may need to go back to a previous version. A good CMS will have built-in version control that allows you to revert to any version of the content you are working on.
The same goes for backups. Does the CMS automatically create backups or is that a function you have to add on with a plugin?
#4 – Publishing Controls
Most companies will have teams of people with different roles. Your CMS needs to have the ability to assign different roles to different people. These might include administrator, author, editor, and contributor (to mention just some).
#5 – SEO Friendly
Is the CMS optimized for SEO? Does it create SEO-friendly permalinks? Does it result in bloated code that slows down the load time of your web pages? Does the CMS come with tools that help you optimize meta tags, such as title tag and meta description? If not, does it allow you to install third-party SEO plugins?
#6 – Detailed Analytics
Does it have built-in SEO analytics that allows you to monitor the performance of your content in the search results? If not, does it allow you to add on extensions or plugins that will do this?
#7 – Security
The security of a website depends only in part on the core CMS features. Add-ons, plugins, and other extensions can be a potential entry point for cyberattacks. And the security of your
The more people there are using a given CMS, the more likely it is that hackers will target that platform. For this reason, some people choose smaller CMS platforms with less market penetration.
On the other hand, CMS platforms with large numbers of users can afford to monitor and update security.
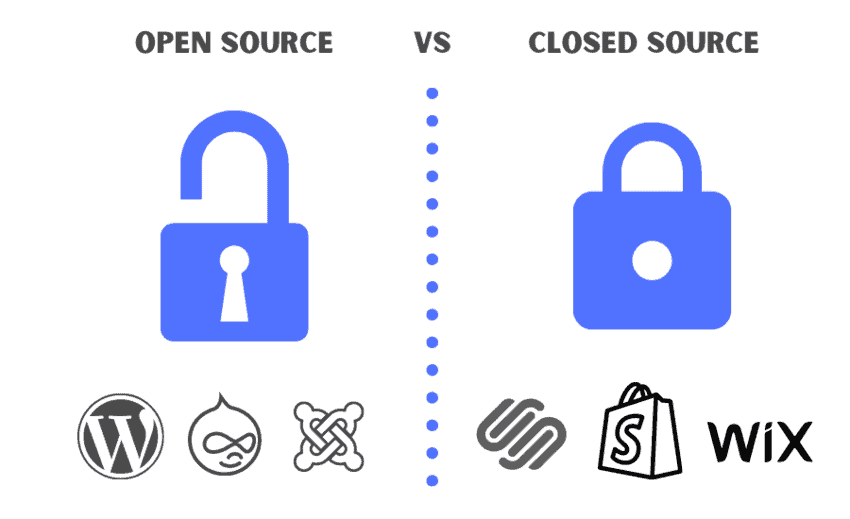
Open vs Closed Source CMS
Content management systems are either open source or closed source. Here are some of the main differences between the two.
An open-source CMS:
- is one where the code is open to the public – developers can use and modify the code.
- often have more extensions and plugins because they result in large communities of developers.
A closed-source CMS:
- is one where the software is private and cannot be modified. With a closed source CMS, you pay a license to use it.
- usually has dedicated support. With open-source CMS, by contrast, there’s no guaranteed support except what you find in online forums.
- is often more secure than an open-source CMS. This is because a closed source CMS has a far smaller user base and is therefore less likely to be targeted by hackers.
Examples of CMS Platforms
1. WordPress
WordPress (WP) is by far the most popular CMS, powering 39.6% of all websites, globally.
WP is open source, which means that it has produced an entire ecosystem of themes and plugins to choose from. At time of writing, there are at least 31,000 WP themes available. There are 59,427 free plugins and thousand more paid plugins. This is the largest collection of themes and plugins of any CMS.
Because of its powerful media management tools, WordPress is the CMS favored by bloggers. But it is also used by large corporate websites, and in particular by large news sites such as CNN.
WordPress gives you complete control over how your website looks, with no limit to the customizations you can make.
Because WP is open source it has produced a large and supportive community. That means that if you run into trouble, you can easily get help in one of the many WP forums.
WordPress is also known for being well optimized for SEO. This is due to its SEO-friendly URLs and its use of categories and tags for blog posts.
2. Joomla
Joomla is one of the three most popular open-source CMS platforms (the other two being WordPress and Drupal). In terms of learning curve, Joomla stands somewhere between WordPress and Drupal: it’s more complex than WP but easier than Drupal. To get Joomla to do exactly what you want, you may need to hire a developer.
Joomla excels in the area of user permissions and so it’s often the CMS of choice for people building membership sites.
There are over 2 million websites using Joomla. It has an active community of developers who have created over 10,000 extensions that extend the functionality of Joomla’s core.

3. Drupal
Drupal is another popular open-source CMS but is more complex than either WordPress or Joomla.
Drupal is highly flexible and very secure. That’s why it’s a popular choice amongst banks, healthcare facilities, and government organizations. It has very good user management features that give a high level of control over users and permissions.
However, Drupal is not beginner-friendly and is best suited to developers and people who know how to code.
That said, Drupal is highly customizable. It’s ideal if you are setting out to build a large site with lots of functionality.
Drupal has an active community that has built over 40,000 modules that extend the functionality of the core CMS.
4. Squarespace
Squarespace is an ideal CMS for beginners – it’s very intuitive and has a very easy-to-use website builder. Squarespace is particularly suited to visual content and is known for its beautiful designs. The platform is favored by creative professionals and by restaurants and entrepreneurs.
Squarespace is not open source and you can’t download it and install it on your own server. Squarespace is an all-in-one service that includes the CMS, web hosting, domain name, SSL certificate, and extensions.
Because it’s not open source, Squarespace is not as flexible as some other CMS platforms. But that’s precisely why it appeals to beginners and people who don’t want to get involved in coding.
5. Magento
Magento is an eCommerce CMS owned by Adobe. Unusually for an eCommerce CMS, Magento is open source. This makes it very flexible – with Magento you can get your website to do virtually anything you want.
Magento is not for beginners, however. It’s mostly used in a B2B context for companies that want a complete customization of their website.
You can extend the core functions of Magento with over 3,800 add-ons that are available in Magento’s Extension marketplace.
6. Shopify
Shopify is primarily an eCommerce CMS, though you can also use it to run a blog, create and edit content, and build landing pages.
It’s ideal for beginners because it’s an all-in-one solution: Shopify provides the hosting as well as the CMS.
With Shopify, it’s quick and easy to get your online store up and running. No coding is required and you won’t need the help of a developer. You also don’t need to worry about security and maintenance – these are both taken care of by Shopify.
The downside to this simplicity and ease of use is that there’s a limit to what you can customize. And because it’s closed-source, you can’t modify the code.
Shopify offers 24/7 support through live chat, email, and phone. There’s also plenty of documentation, including written guides and video tutorials.
You can extend the core functions of Shopify using over 4,000 add-on apps.
Through Shopify payments, you can automatically accept credit cards and debit cards.
7. Wix
Wix is another CMS that comes as part of an all-in-one package with built-in hosting. Although Wix is a content management system, it is known primarily as a website builder.
Wix is one of the easiest to use website builders available. It has an intuitive drag-and-drop interface. And that makes it a popular choice for people who want to get their site up and running quickly, without any complications.
You can build a site for free on Wix but your site will have a Wix subdomain and will also show ads by Wix. To remove the ads and use your own domain, you’ll have to upgrade to a paid plan.
Many people who start off on Wix eventually find the platform too limiting and move over to WordPress.
When building your site on Wix, there are hundreds of templates to choose from. Alternatively, you can use the Wix Artificial Design Intelligence (ADI) to build a site for you.
Although you can use Wix for eCommerce, it’s not a great choice for running an online store, as it’s very limited in its options. For example, you can only accept payments using PayPal or Authorize.net.
Conclusion
A content management system (CMS) is software that allows you to build a website and manage your online content without having to do any coding.
The CMS that is right for you will depend on your needs. But a good ‘all round’ CMS that is not difficult to use but very flexible is WordPress. And that’s why it powers more websites than any other CMS on the market.