Link building is an area of SEO where you can easily get on the wrong side of the Google algorithm.
This article gives you 10 link building do’s and don’ts.
- #1. Do – Create Valuable Content
- #2. Do – Disavow Toxic Backlinks
- #3. Don’t – Pay For Backlinks
- #4. Don’t – Offer to Sell Backlinks
- #5. Don’t – Get Links from Irrelevant Websites
- #6. Don’t – Create Low-Value, Self-Built Backlinks
- #7. Don’t – Get Backlinks from Link Farms
- #8. Don’t – Get Involved in Link Exchanges
- #9. Don’t – Use Private Blog Networks
- #10. Don’t – Only Build Backlinks to Your Homepage
- Conclusion
- More Articles About Link Building

#1. Do – Create Valuable Content
The best way to build quality backlinks is to publish content that people want to link to. Link-worthy content is the starting point for good link building.
That means writing detailed and well-researched articles. The kind of content that other websites will link to includes:
- Guides
- Tutorials
- Interviews with Experts
- Statistics-based articles
- Case Studies
- Infographics
As a rule of thumb, the more research you do, the more original your content becomes and the more likely people will link to it.
#2. Do – Disavow Toxic Backlinks
As your website gains authority and visibility in the search engines, you will inevitably attract toxic backlinks.
Toxic backlinks are links from websites that are not designed to educate, inform, or even entertain. They are created purely for ‘black hat’ purposes and are never even visited by real people.
Here’s a useful guide on how to spot toxic backlinks.
So why does your website attract these kinds of links? It’s a question we’ve all asked ourselves, at one time or another.
Sometimes it is due to ‘negative SEO’.
That’s where a competitor tries to damage your rankings by directing low quality backlinks to your website. Alternatively, toxic links can come from people who want to charge you a fee to have them removed.
Wherever they come from, links from spammy websites will damage the SEO of your website.
Ideally, you should ask the linking websites to remove your link. But very often they will ask for a fee to remove the backlink. That, after all, is why they linked to you in the first place.
Google has provided a remedy to this: the Google disavow tool. When you upload a list of linking websites that you want to disavow, Google will ignore the links pointing to your site from those spammy websites.
You can identify toxic backlinks and disavow them in SEO tools such as Ahrefs, SEMrush, and Monitor Backlinks.
#3. Don’t – Pay For Backlinks
Never pay for backlinks.
Paying for backlinks is a direct contravention of Google’s Webmaster Guidelines. To see the guidelines specific to link building, scroll down to the section titled ‘participating in link schemes’:
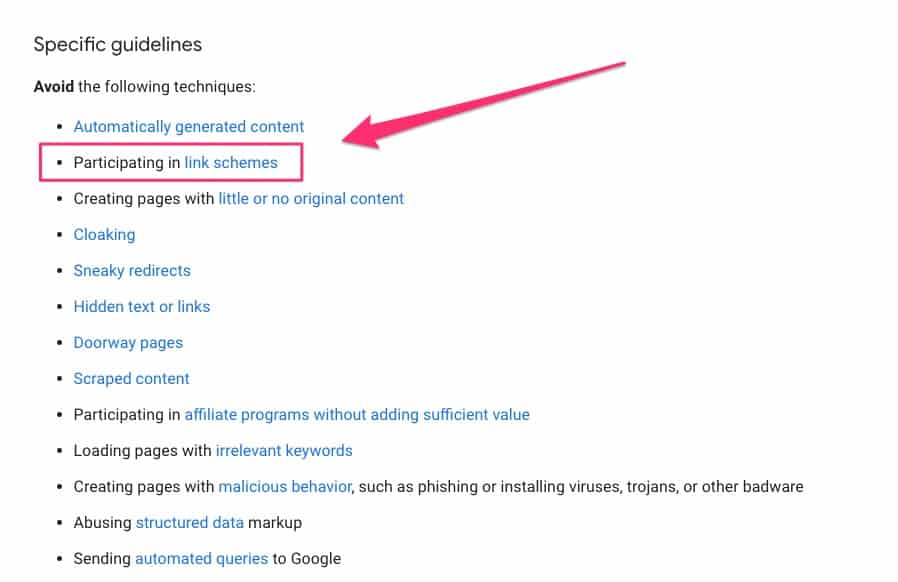
Paid backlinks are always low quality and spammy.
More likely than not, the websites involved in paid backlinks will already be on Google’s radar and by purchasing such links, you simply add your website to a list of ‘dodgy’ domains. You could even earn yourself a Google penalty.
#4. Don’t – Offer to Sell Backlinks
The practice of selling (or buying) backlinks is expressly forbidden by Google’s Webmaster Guidelines. If you get caught doing this, expect a penalty from Google.
#5. Don’t – Get Links from Irrelevant Websites
Google uses backlinks to assess the relevance and authority of a piece of content. And that’s why links for irrelevant websites won’t help your website rank higher.
For example, if your website is about baking bread and you get a backlink from a skin cancer clinic, that’s not a relevant link and it won’t help your website perform better in the search results.
#6. Don’t – Create Low-Value, Self-Built Backlinks
Self-built links are backlinks that you create by commenting on blog posts and forums, signing guest books etc.
Google considers these kinds of backlinks low-value, because they were created by you (remember: backlinks are important to Google because they act like a vote of confidence in you from other people).
If you do enough of this kind of link-building, it could even result in an algorithmic penalty.
#7. Don’t – Get Backlinks from Link Farms
Web pages with more than a 100 external links look to search engine algorithms like pages that have been set up for the purpose of selling links.
Backlinks from these kinds of pages will only harm your SEO.
#8. Don’t – Get Involved in Link Exchanges
Don’t get involved in any kind of link exchange (however indirect), as this falls under the heading ‘link schemes’ in Google’s Webmaster Guidelines.
Remember: everything you do on the internet leaves a digital footprint that can eventually be detected by the algorithms.
#9. Don’t – Use Private Blog Networks
PBNs or Private Blog Networks are a network of websites owned by the same individual.
Typically, someone buys high authority aged domains, then places some relevant content on those domains.
They then insert links from those websites to their main website.
This way, they give their main website a high domain authority almost overnight.
PBNs are hard for Google to detect. But if you get caught using PBN’s, you can expect a Google penalty.
#10. Don’t – Only Build Backlinks to Your Homepage
You want your links to look (and be) as natural as possible.
When people link to other websites, it’s usually because of a particular article on that website. And that means that natural links are mostly not to a home page.
If most of your backlinks are to your home page, that will create an ‘unnatural’ link profile: it’s much better to have backlinks pointing to individual pages on your website.
For more information about what is a natural backlink, see this article by Adam Riemer.
Conclusion
Link building is an area of SEO that can easily stray into ‘black hat’ territory. The consequences of participating in ‘link schemes’ or other practices forbidden by Google can be severe and hard to undo.
Hopefully, these 10 link building do’s and don’ts will help you stay on the right side of Google’s Webmaster Guidelines.